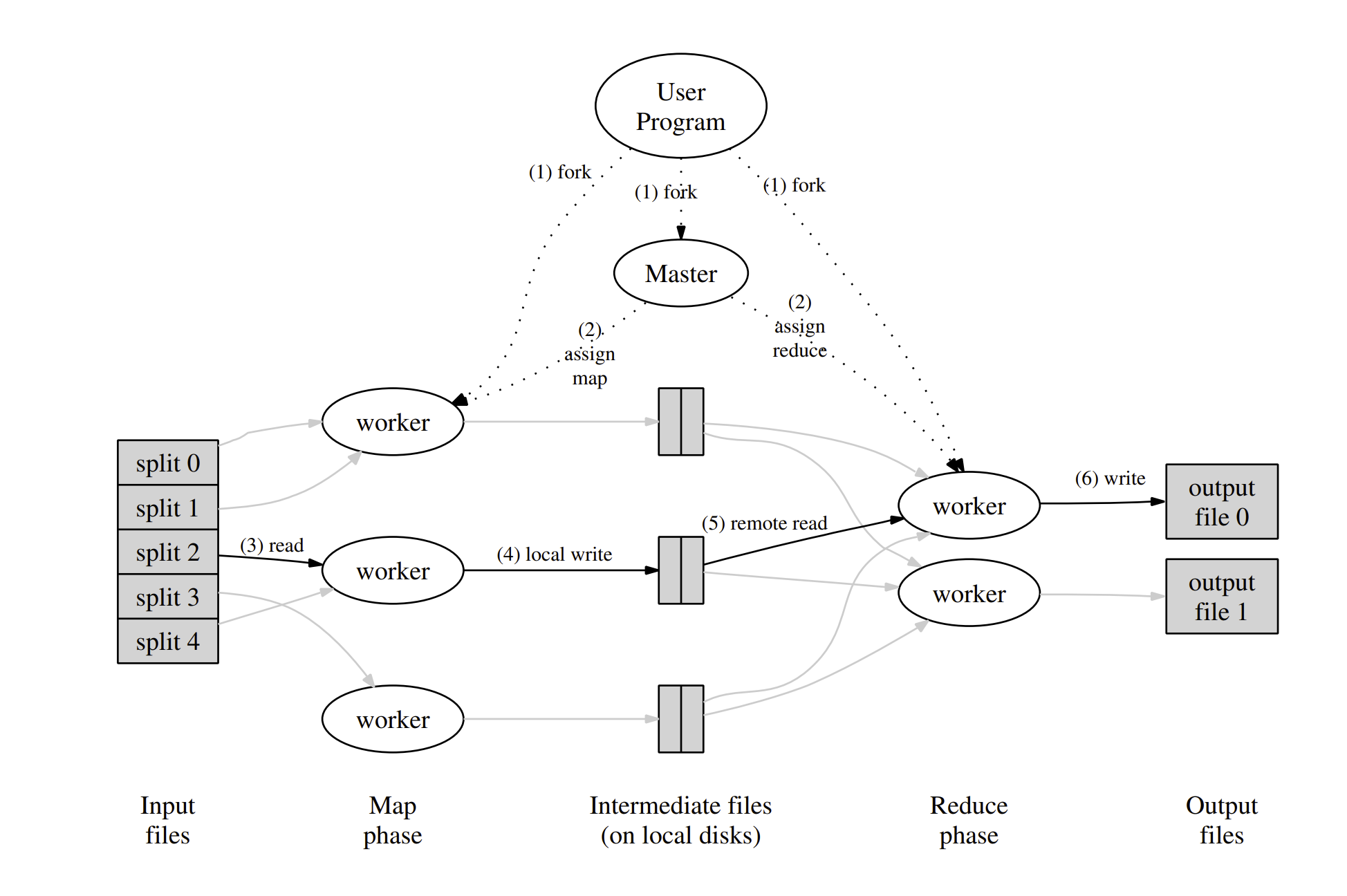
System Design - Map Reduce System
MapReduce is a programming model for processing big data sets by parallel, distributed algorithm on a cluster. There are a few key words in the above description:
- Big data sets: that means it is not possible processed by a single machine/host;
- Parallel/distributed: that means a cluster of machine/hosts would process a set of data concurrently;
- Programming model: this is a model for process different types of data.
Since the data sets are big and it is not possible processed by a single host, we have to distribute the data to different machines/hosts, and this is done by splitting the large data sets into many chunks. And each of the chunks is processed by one host.
As the name suggested, there are two types of works, Map and Reduce for the data sets.
- Map work: it is like the name suggested to map key in the data sets to a value and thus generate a key/value pair for each key in the data sets. Similar to the map function in Python or JavaScript.
- Reduce work: it is to aggregate a list of key/value pairs using some sort of operators. For example, count the number of times a key appears.
- Shuffer/Partition work: An additional procedure between Map and Reduce normally required to arrange the same key to the same node/file, this is called shuffer or partition. Partition makes more sense since it is to partition the keys to different reducer nodes. Using hash(key) would generate this effect.
Most of data processing could be decomposed into this the above procedures and therefore could be modeled by MapReduce programming model. For example:
- Count words in documents:
- Map: Read the documents word by word. Generate Key/Value pairs with key the word, value always 1. Repeat word store multiple times.
- Shuffer/Partition: Using hash to send the all key/value pairs to different nodes/files. So that each node/file would receive all the keys from different map work.
- Reduce: Aggregate the number of the same word and output the total numbers of each word.
- Inverted Index:
- Map: Parse each documents and generate Key/Value pair as <word, document ID>;
- Shuffer/Partition: Send each key/value pairt to different nodes/files using hash(word);
- Reduce: Aggregate all document id for a word and output <word, List
>.
- Distributed Sort:
- Map: Generate key/value pair from each record, only key is required here actually;
- Shuffer/Partition: The trick is on the partition, the same key is sent to the same reducer node obviously. But the key/value is sent the particular reducers. For example: All keys start with A are sent to reducer 1, B to 2, C to 3…. Similar to bucket sort.
- Reducer: Each reducer node sorts the keys it has.
Since this is a distributed parallel process, there must be a host to allocate and coordinate all these map/partition/reducer works.
The above picture is from the seminal paper of Map Reduce. It shows how each worker node and master coordinate their work. There are two modes of coordination:
- Push: Master constantly checkes if the workers are working on jobs. If not, master assign a job to worker.
- Pull: Whenever workers are idle, it asks for jobs from master, and if master has some jobs, then it assigns to the worker.