Algorithm & Data Structure - Substring with Bit Mask
A number of substring problems could be solved by bit mask with conversion to similar as subarray sum problems. Basic subarray sum equals K could be soved by hashmap in O(n):
- Store number of prefix sum in hashmap.
- Get the number of current running sum - K.
- LeetCode - 560
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
int count = 0, sum = 0;
HashMap<Integer, Integer> sumMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
sumMap.put(sum,1);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum += nums[i];
if (sumMap.containsKey(sum - k))
count += sumMap.get(sum-k);
sumMap.put(sum, sumMap.getOrDefault(sum, 0)+1);
}
return count;
}
Similary approach could be applied to a few substring problem with the help of bitmask. Bitmask is able to convert the substring to a number, and store it in the hashmap, especially if the problem requires to find even or odd number of characters.
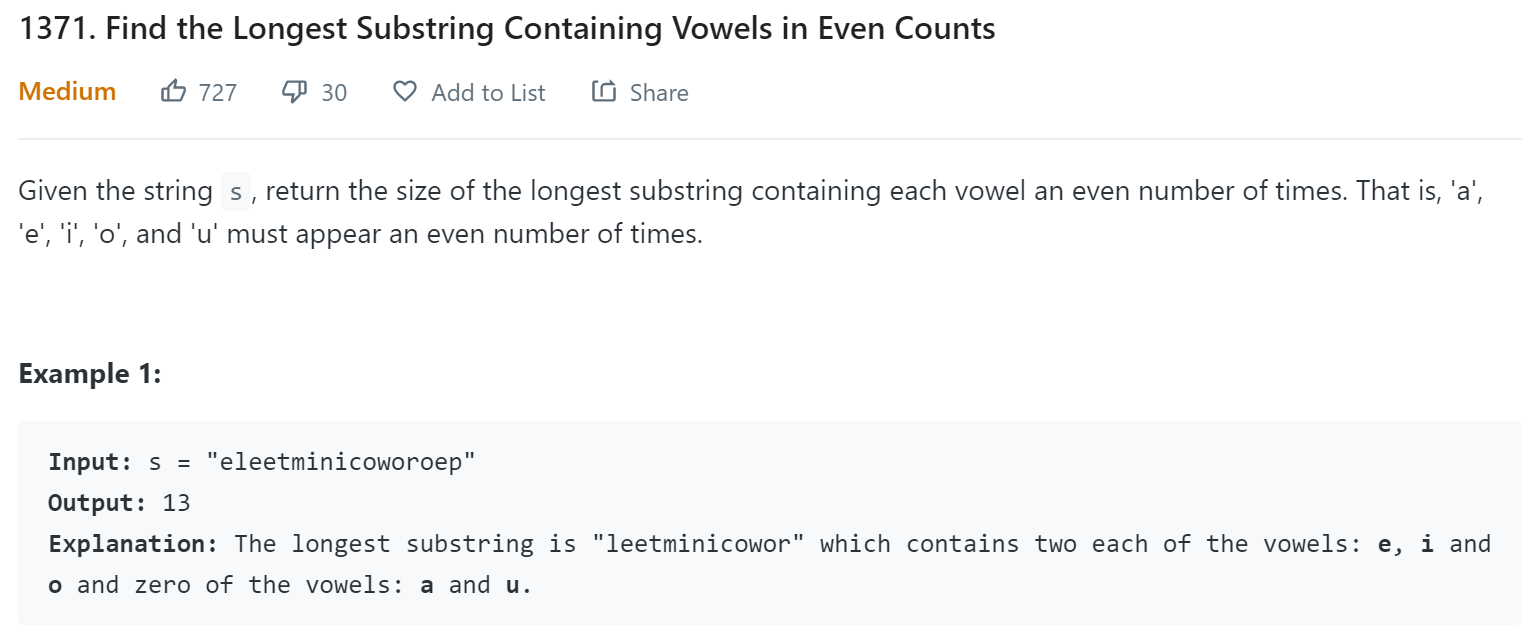
- LeetCode - 1371
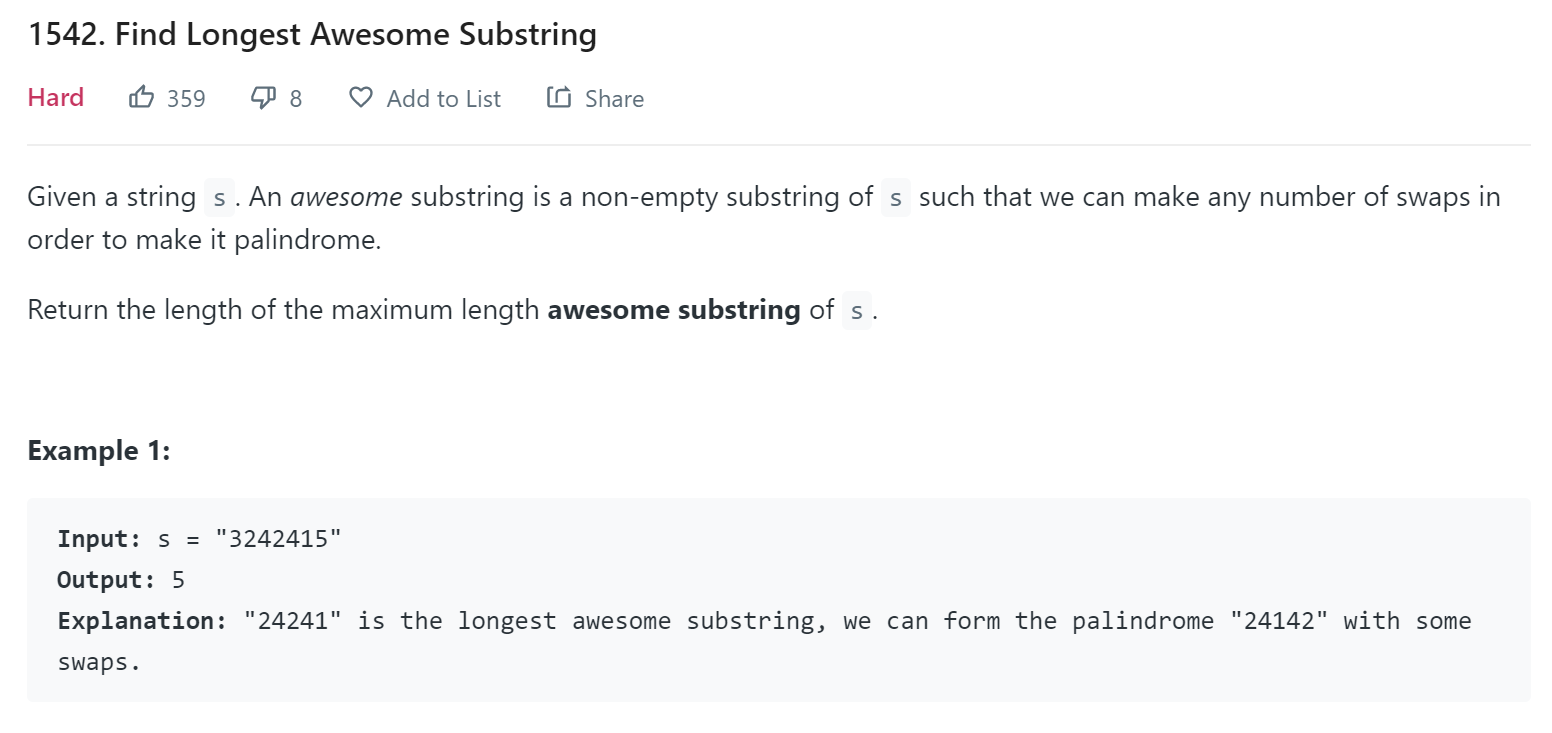
- LeetCode - 1542
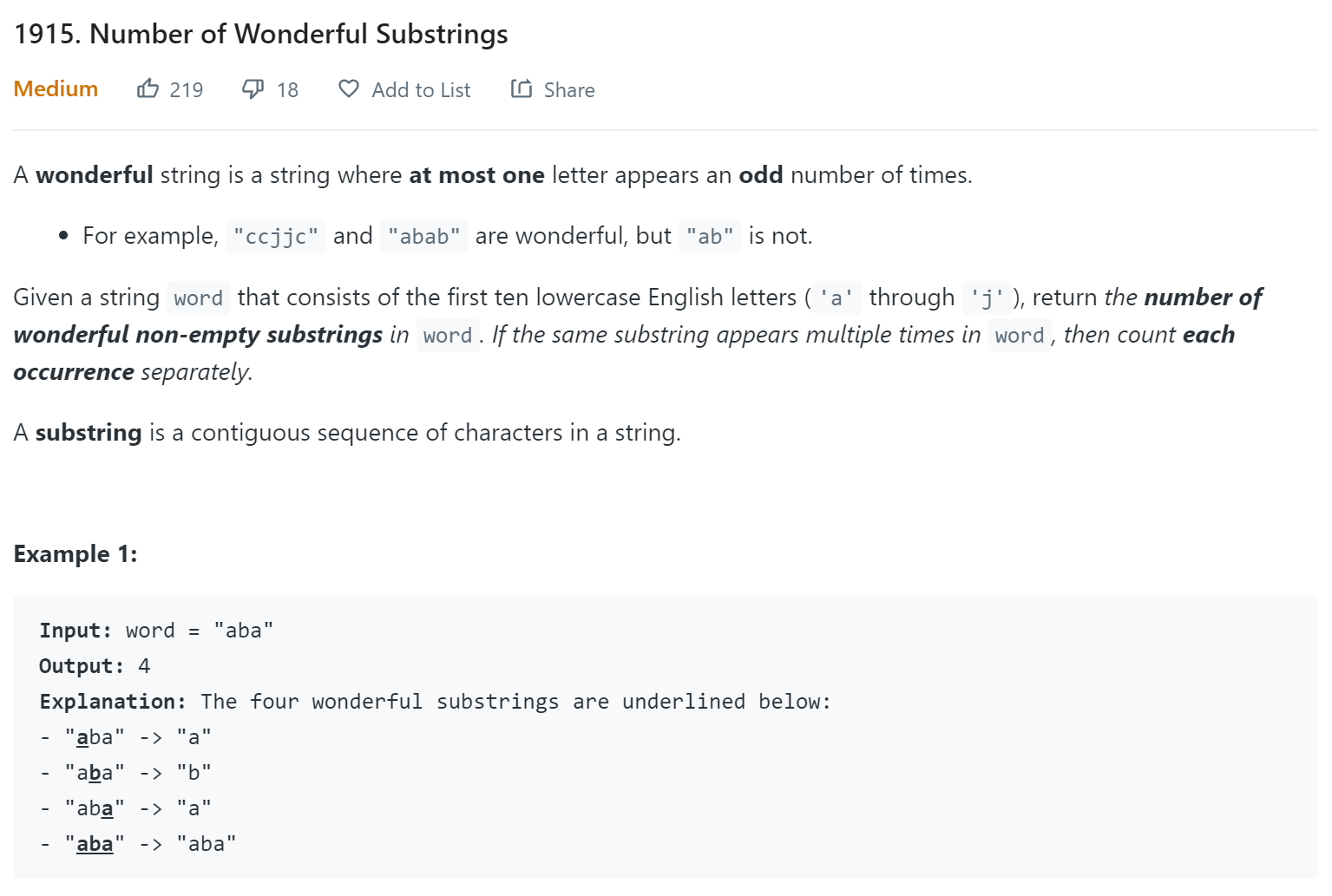
- LeetCode - 1915
Because we only care even or odd number of characters, we could use bitmask to reverse the bit with 0 or 1, i.e., if the number of character is even, set it to 0, else set it to 1. A bit operation XOR could achieve it easily. We only need to XOR the bit if we see the corresponding character. Because the string only include lowercase letter, we could fit all the letters to a 32 bit integer.
We reverse its bit whenever we see a vowel. If two positions \(i\) and \(j\) have the see bit pattern (mask), that means, substring [i+1….j] has even number of vowels. Why? because if a vowel’s bit is 0 at both positions, this means from [0…i] and [0…j], the letter appears even times, so it shoud also be even times from [i+1…j], (even number - even number = even number). If a vowwel’s bit is 1 at both positions, this means from [0…i] and [0…j], the letter appears odd times, so it shoud also be odd times from [i+1…j], (odd number - odd number = even number).
Since we are looking for the max length, we only need to store the first time a mask appears, and for a mask of 0, it means it is position is -1.
public int findTheLongestSubstring(String s) {
int mask = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> vowelCount = new HashMap<>();
vowelCount.put(0,-1);
int length = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c == 'a' || c=='e' || c=='i' || c=='o' || c=='u'){
mask ^= (1<<(c-'a'));
}
if (!vowelCount.containsKey(mask)) {
vowelCount.put(mask, i);
} else {
length = Math.max(length, i - vowelCount.get(mask));
}
}
return length;
}
We use the similar bit mask approach to represent odd or even numbers of each character. We have only 10 digits, so it could fit in a 32 bit integer. We use the same to revers a bit and 0 represents even time, 1 represents odd times so far. Also we only need to record the first time position of a mask.
The biggest difference here is we are not only looking for the position of the same mask, but also the position of a mask with one letter difference. Because, palindrome string could also be formed with an addition letter. How do we achieve this, we could find the mask with one bit different from the map.
public int longestAwesome(String s) {
int mask = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> digitCount = new HashMap<>();
digitCount.put(0, -1);
int length = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
mask ^= (1<<(s.charAt(i)-'0'));
//find the first position with the same mask
length = Math.max(length, i - digitCount.getOrDefault(mask, i);
// find the first position with one bit difference
for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
length = Math.max(length, i - digitCount.getOrDefault(mask^(1<<k), i));
}
if (!digitCount.containsKey(mask))
digitCount.put(mask, i);
}
return length;
}
This is more close to Leetcode-1542 because the similar 10 letters and allow one odd difference. But this problem requires the record the number of time a mask appeared. So it is similar to subarray sum equals K problem above.
public long wonderfulSubstrings(String word) {
Map<Integer, Integer> maskCount = new HashMap<>();
maskCount.put(0,1);
int mask = 0;
long count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
mask ^= 1<<(c-'a');
count += maskCount.getOrDefault(mask,0);
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
count += maskCount.getOrDefault(mask^(1<<j),0);
}
maskCount.put(mask, maskCount.getOrDefault(mask,0)+1);
}
return count;
}