Authentication - Session and JWT
Session based authentication
In the session based authentication, the server creates a session for each of the user after user logined in, and send the session Id to client browser. The client browser kept the session Id in its cookie. Whenever the client send info to server, it brings the cookie with session Id. The server then could verify the client session Id with the session in its memory.
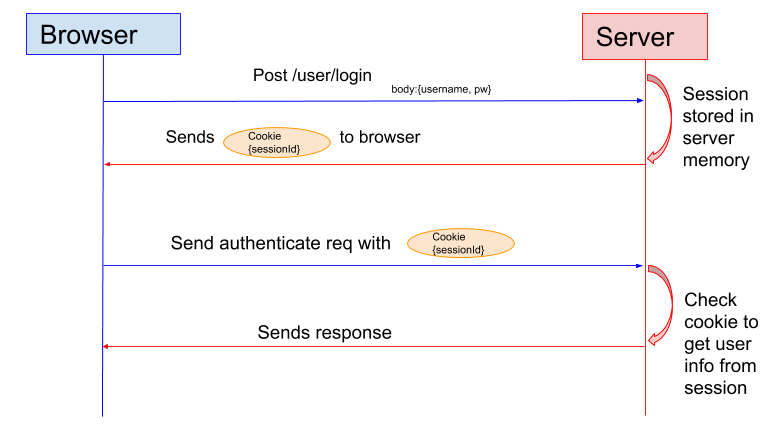
An example of session Id that saved in the browser is as below picture:
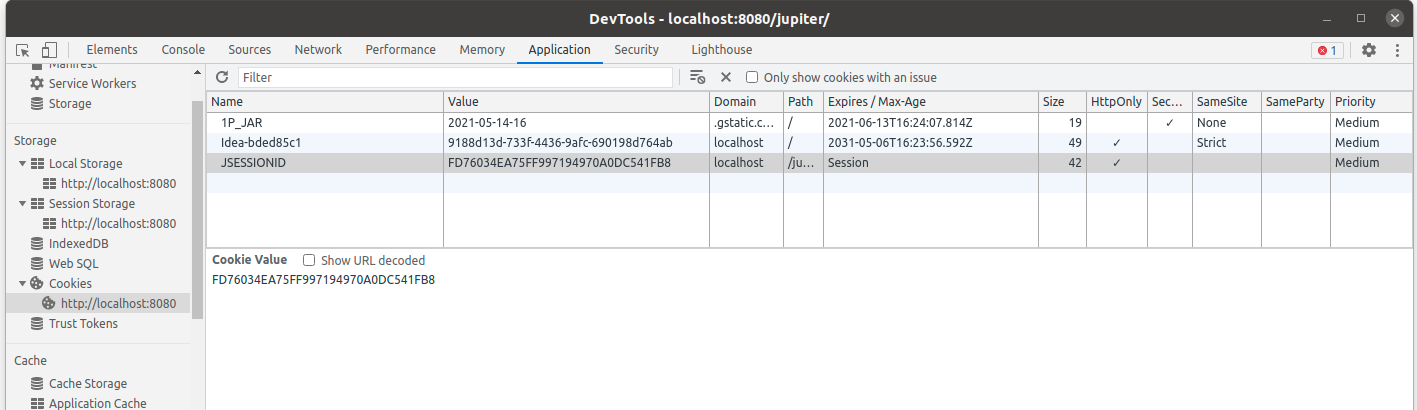
An example of using session is as below,
HttpSession session = request.getSession(); // if no session, create one
session.setAttribute("user_id", body.userId);
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(300); //set session timeout in seconds
loginResponseBody = new LoginResponseBody("OK", body.userId, conn.getFullname(body.userId));
The Session Id is added to the headers by server hoster (e.g., Tomcat), but not by GET or POST request.
To verify the sessionId, the code below could be use:
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); // get session from the request
// if no session exist, return 403
if (session == null) {
response.setStatus(403);
mapper.writeValue(response.getWriter(), new ResultResponse("Session Invalid"));
return;
}
JWT based authentication
JWT is JSON Web Token. In token based authentication, the server creates token with a secret and sends it to the client. The client stores JWT and includes JWT in the header with every request. JWT is consisted of three parts: Header, Payload, and Signature, and they are encrypted to a string. The token is saved in client side only, where the server only provide code and decode algorithm. The advantage of Token based authentication is the server doesnot need to store any client information. This improves scalability.
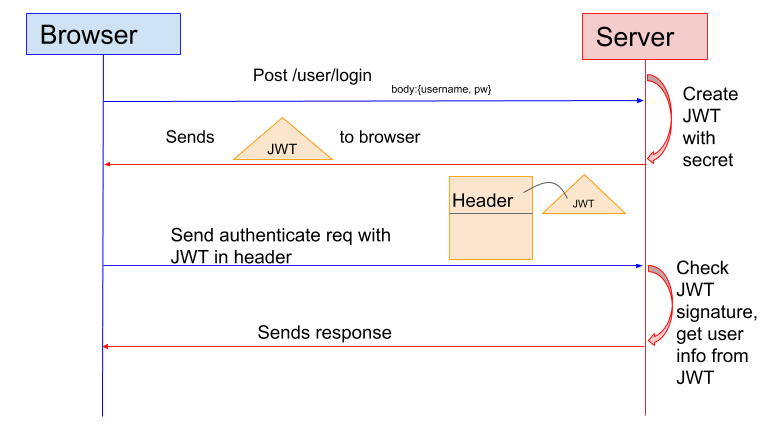
On the client side, the token could be stored in local memory, cookies, and web storage. Below is one example that use cookie to store the token:
Encode to jwt token
if (conn.verifyLogin(body.userId, body.password)) {
try {
// encode to jwt token, using java-jwt
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256("secret");
String token = JWT.create()
.withIssuer("auth0")
.sign(algorithm);
Cookie accessToken = new Cookie("access_token", token);
response.addCookie(accessToken);
} catch (JWTCreationException exception){
// do something if encode fails
}
loginResponseBody = new LoginResponseBody("OK", body.userId, conn.getFullname(body.userId));
}
Verify the token
String jwtToken = "";
for (Cookie cookie : request.getCookies())
{
if (cookie.getName().equals("access_token")) {
jwtToken = cookie.getValue();
}
}
try {
Algorithm algorithm = Algorithm.HMAC256("secret");
JWTVerifier verifier = JWT.require(algorithm)
.withIssuer("auth0")
.build(); //Reusable verifier instance
DecodedJWT jwt = verifier.verify(jwtToken);
} catch (JWTVerificationException exception){
response.setStatus(403);
mapper.writeValue(response.getWriter(), new ResultResponse("Invalid Token"));
return;
}
