Algorithm & Data Structure - Next Permutation
Next permutation is a number arragement that generating a number only more than the current one. For example, for numbers 1, 2, 3, the combinations could be:
[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]
The above lists the combinations in order, so for each of the combination, the next permutation is the one next to it. Given a combination, how to find the next combination that greater the current one. This is the next permutation problem. Of cause, you could search by list all combinations, but that is time comsuming.
- LeetCode - 31, 556
Both problems are the same, one using number combination, the other uses character combination.
First, the smallest combination is obviously with increasing order, and the biggest combination is with decreasing order. For example, [1, 2, 3] and [3, 2, 1]. This is also true for any subarray. We can find the maximum subarray from end, and the next greater combination should be more it. For example, if the subarray from the end is […..1, 3, 2, 1], then we can only change the number before 3 a bigger numer, i.e., make 1 to be a bigger number.
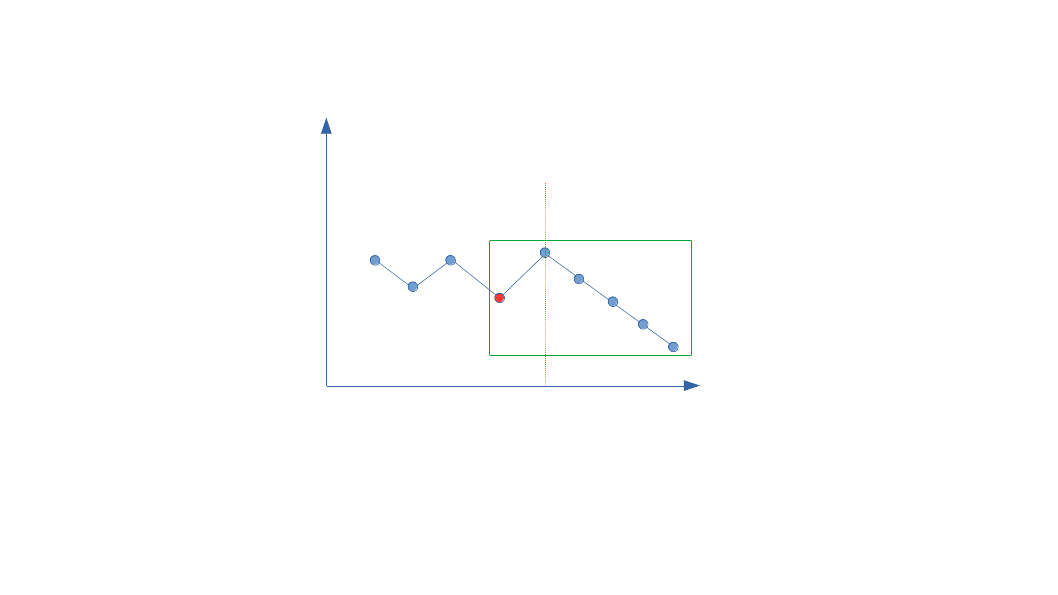
How do we arrange the numbers?
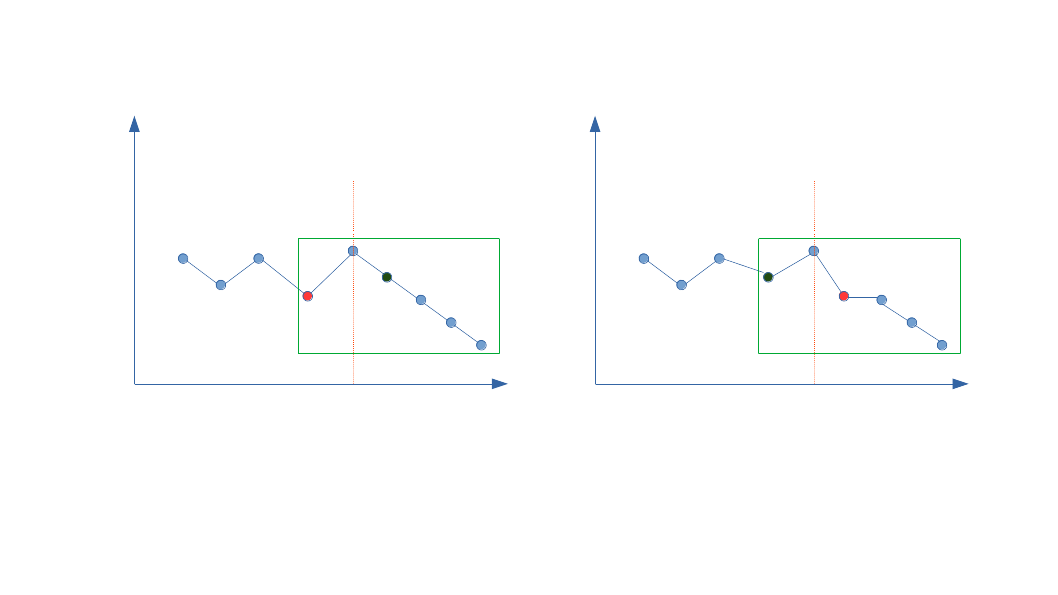
Let’s focus on the subarray that we just found as shown in below picture. We know that we have to rearrange this array to get the next greater combination. First, we need to replace the first element in the subarray to be next greater element in the subarray, i.e., replace the red one with the blue one, see picture below. Now this subcombination is greater than the previous one, but is it the next greater, i.e., [2, 3, 1, 1] is greater than [1, 3, 2, 1], but there are still numbers in between. We mentioned that the smallest combination is increasing order, since we changed 1 to 2, we need the smallest combination with 2. We can sort the subarray, but notice the array is alreadey sorted in reversed order, we just need to reverse it again.
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int i = nums.length - 2;
// find the first non decreasing element from the end
//
for (; i >= 0; i--) {
if (nums[i] < nums[i+1]) {
break;
}
}
if (i == -1) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return;
}
// replace the element with a greater element from the subarray
for (int j = nums.length - 1; j > i; j--) {
if (nums[j] > nums[i]) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
break;
}
}
int k = nums.length - 1; i = i+1;
// reorder/reverse the subarray
while (i < k) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[k];
nums[k] = temp;
i++;
k--;
}
}
